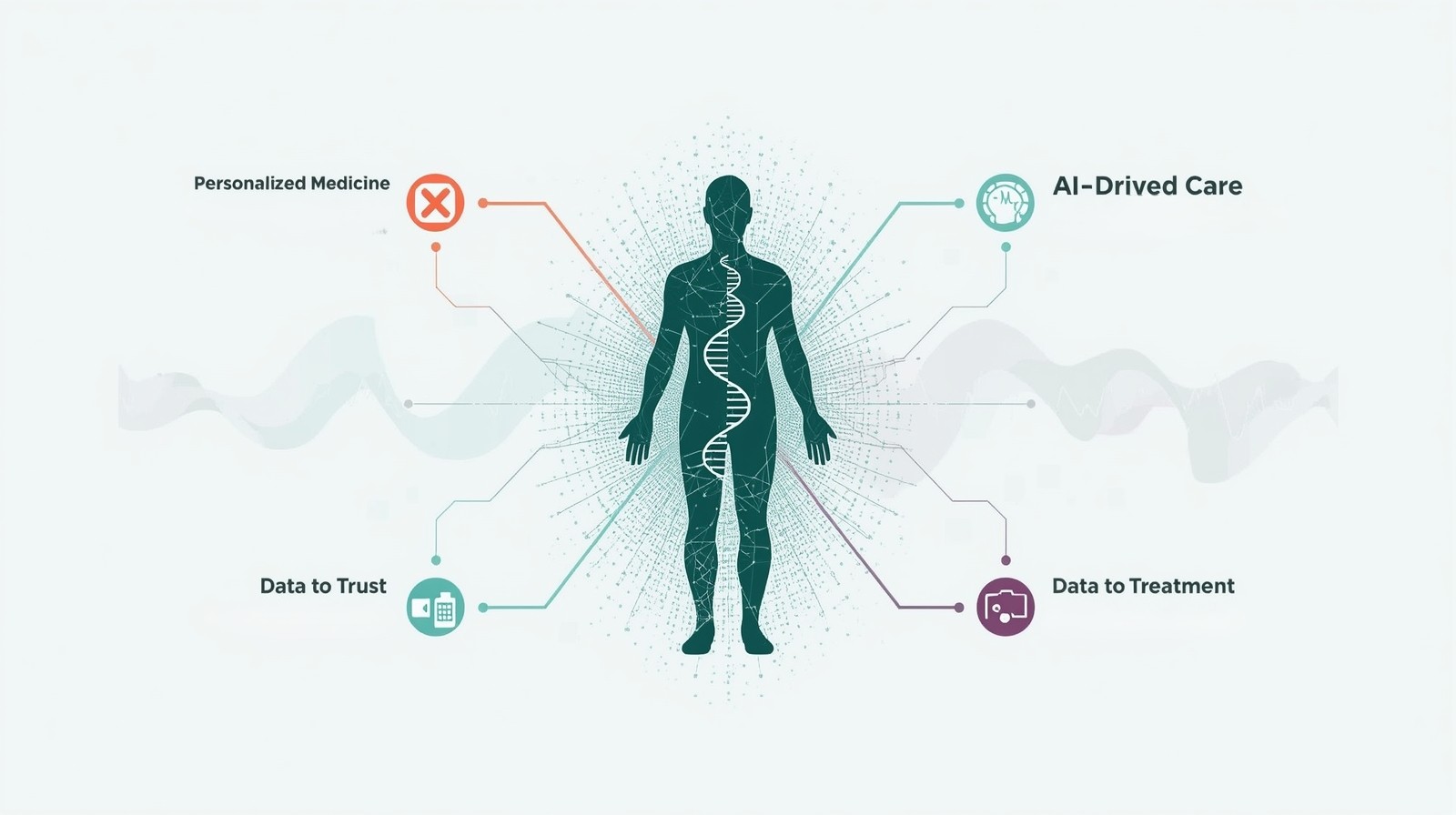
AI in Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Better Treatments
Imagine walking into your doctor’s office and receiving a treatment plan designed specifically for you—not based on general guidelines, but on your unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health history. The Role of AI in Personalized Medicine is making this vision a reality, transforming healthcare from a one-size-fits-all approach to truly individualized care. As someone deeply invested in AI ethics and digital safety, I want to guide you through understanding how this technology works, why it is relevant for your health, and how you can benefit from it safely and responsibly.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn the fundamentals of AI-powered personalized medicine, discover how it analyzes your health data, and gain practical steps to engage with these innovations while protecting your privacy. Whether you’re a patient curious about new treatment options or simply interested in healthcare’s future, this article will empower you with knowledge to make informed decisions about your care.
Understanding Personalized Medicine and AI’s Revolutionary Role
Personalized medicine, also called precision medicine, represents a fundamental shift in healthcare philosophy. Instead of treating diseases based on average patient responses, it tailors medical decisions and treatments to individual characteristics. The Role of AI in Personalized Medicine amplifies this approach by processing vast amounts of health data—from genomic sequences to lifestyle patterns—that would be impossible for humans to analyze comprehensively.
Traditional medicine often relies on clinical trials showing what works for most people. But “most people” doesn’t necessarily include you. Your genetic variations might make you metabolize certain drugs differently, or your specific disease markers might respond better to alternative treatments. AI systems excel at identifying these nuanced patterns by examining thousands of variables simultaneously, creating a complete picture of your unique health profile.
What makes AI particularly powerful in this context is its ability to learn continuously. As more patients receive personalized treatments and their outcomes are recorded, AI algorithms become increasingly accurate at predicting which interventions will work best for similar individuals. This creates a virtuous cycle where personalized medicine becomes more precise with each patient it helps.
How AI Analyzes Your Health Data to Create Custom Treatment Plans
The journey from data collection to personalized treatment recommendations involves several sophisticated AI processes working together. Understanding these steps helps you appreciate both the technology’s potential and the importance of data security throughout.
Step 1: Comprehensive Data Collection
AI-powered personalized medicine begins with gathering diverse health information about you. This includes:
- Genomic data: Your DNA sequence, which reveals genetic predispositions and how you might respond to specific medications
- Clinical records: Your medical history, previous diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes
- Lifestyle information: Diet, exercise patterns, sleep quality, stress levels, and environmental exposures
- Real-time monitoring data: Information from wearable devices tracking heart rate, activity, glucose levels, and other biomarkers
- Imaging results: X-rays, MRIs, CT scans analyzed for subtle patterns indicating disease progression or treatment response
This step matters because comprehensive data provides the foundation for accurate predictions. However, it’s crucial that you understand what data is being collected and maintain control over who accesses it. Always ask your healthcare provider about their data protection policies and ensure you’re comfortable with how your information will be used.
Step 2: Pattern Recognition Through Machine Learning
Once collected, your data flows into machine learning algorithms trained on millions of similar health records. These AI systems identify patterns invisible to human observation. For instance, they might detect that patients with your specific genetic markers, combined with certain lifestyle factors, respond exceptionally well to a particular drug dosage.
The AI doesn’t just look at obvious connections—it explores multidimensional relationships between hundreds of variables. It might discover that your vitamin D levels, combined with specific gene variants and exercise habits, influence how your body responds to immunotherapy treatments. This holistic analysis reveals treatment opportunities that traditional approaches would miss.
Why this step is important: Machine learning eliminates human bias and cognitive limitations. A doctor can realistically consider maybe 5-10 key factors when prescribing treatment. AI can simultaneously evaluate thousands, ensuring nothing important slips through the cracks.
Step 3: Predictive Modeling for Treatment Outcomes
After identifying relevant patterns, AI creates predictive models specifically for your situation. These models forecast:
- Which treatments are most likely to be effective for you
- Potential side effects based on your genetic profile
- Optimal drug dosages accounting for your metabolism
- Disease progression timelines unique to your case
- Preventive interventions that could stop problems before they start
AI doesn’t simply recommend the “best” treatment in general—it ranks options specifically for your probability of success. This means you and your doctor can make truly informed decisions, weighing effectiveness against potential risks tailored to your individual profile.
This step emphasizes why AI ethics matters so deeply in medicine. These predictions significantly influence your treatment path, making algorithm transparency and fairness critical. Responsible AI systems should explain their reasoning and allow medical professionals to verify recommendations against clinical expertise.
Step 4: Continuous Monitoring and Treatment Adjustment
Personalized medicine AI doesn’t stop after initial recommendations. Advanced systems continuously monitor your treatment response through:
- Regular analysis of biomarker changes
- Tracking symptoms and quality of life indicators
- Comparing your progress against predicted outcomes
- Identifying early warning signs of complications
If your response differs from predictions, the AI alerts your healthcare team and suggests adjustments. This creates a dynamic treatment approach that evolves with your changing health status rather than following a rigid predetermined plan.
Why continuous monitoring matters: Diseases and bodies change over time. What works initially might become less effective, or side effects might emerge. Real-time AI analysis catches these shifts early, allowing proactive adjustments rather than reactive crisis management.

Real-World Applications: How AI Personalizes Different Treatment Areas
The Role of AI in Personalized Medicine extends across virtually every medical specialty, revolutionizing how we approach disease treatment and prevention. Let me share specific examples that demonstrate this technology’s practical impact.
Cancer Treatment Optimization
Oncology has become one of the most successful applications of personalized AI medicine. Cancer is not a single disease but hundreds of distinct conditions defined by specific genetic mutations. AI systems analyze tumor genomics to identify precisely which mutations drive each patient’s cancer, then match them to targeted therapies most effective against those specific genetic profiles.
For example, two patients might both have lung cancer, but their tumors could have entirely different genetic drivers. Traditional chemotherapy treats both the same way. AI-powered genomic analysis reveals one patient has an EGFR mutation responding to specific targeted drugs, while the other has a different mutation requiring alternative therapy. This precision dramatically improves survival rates while reducing unnecessary toxic treatments.
AI also predicts immunotherapy response—treatments that help your immune system fight cancer. Not all patients benefit from immunotherapy, and these drugs can be expensive with significant side effects. AI analyzes biomarkers, predicting who will respond, sparing non-responders from ineffective treatment while ensuring those who will benefit receive it promptly.
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Management
Heart disease remains a leading cause of death, but AI personalized medicine is transforming how we prevent and treat it. AI algorithms analyze multiple risk factors—genetics, cholesterol patterns, blood pressure trends, lifestyle habits, and inflammation markers—creating individualized cardiovascular risk profiles far more accurate than traditional calculators.
Rather than generic advice to “eat healthy and exercise,” AI-powered systems provide specific recommendations: your genetic profile suggests you metabolize saturated fats poorly, so plant-based protein sources would benefit you particularly; your glucose variability patterns indicate you should prioritize eating protein before carbohydrates; and your stress response patterns suggest morning exercise reduces your cardiovascular risk more effectively than evening workouts.
For patients already diagnosed with heart conditions, AI monitors continuous data from wearable devices, detecting subtle changes in heart rhythm or activity tolerance that might signal deterioration days or weeks before symptoms become obvious. This early warning system prevents emergency situations through timely intervention.
Mental Health Treatment Personalization
Mental health treatment has historically involved trial-and-error medication approaches, but AI is changing this frustrating process. Pharmacogenomics—how your genes affect drug response—combined with AI analysis can predict which antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications will work best for you with minimal side effects.
AI systems also analyze language patterns, activity levels, sleep quality, and social engagement data (when consensually provided) to detect early signs of depression or anxiety episodes. This allows preventive interventions before conditions worsen, potentially avoiding hospitalizations.
Digital mental health platforms use AI to personalize cognitive behavioral therapy exercises, adapting difficulty and focus based on your progress and specific symptom patterns. This creates more effective therapy experiences accessible beyond traditional office visits.
Rare Disease Diagnosis
For patients with rare diseases, diagnosis often takes years as doctors struggle to identify conditions affecting only thousands globally. AI systems trained on comprehensive medical literature and rare disease databases can analyze symptom combinations and genetic data to suggest diagnoses that might never occur to individual physicians.
One powerful example: AI helped diagnose a child with a rare genetic condition by analyzing whole genome sequencing data and comparing it against known disease-causing mutations. The diagnosis took weeks instead of years, allowing immediate treatment that prevented irreversible complications. Without AI’s pattern recognition across millions of genetic variations, this connection might never have been made.
Privacy and Safety: Protecting Your Health Data in AI Systems
As someone specializing in AI ethics and digital safety, I cannot emphasize enough how critical data protection is in personalized medicine. The same detailed health information that makes AI effective also creates significant privacy risks if mishandled. Understanding how to protect yourself while benefiting from these technologies is essential.
Understanding Your Health Data Rights
Before engaging with AI-powered personalized medicine services, know your fundamental rights:
You own your health data. Despite collecting it, healthcare providers and technology companies don’t own your genomic information, medical records, or health metrics. You have the right to access your complete data, understand how it’s used, and request corrections if information is inaccurate.
You control data sharing. With limited exceptions (public health emergencies, legal requirements), you decide who accesses your health information. Before any AI analysis, you should receive clear explanations of what data will be used, who will access it, and whether it will be shared with third parties.
You can withdraw consent. If you initially agreed to data sharing for research or AI analysis but later change your mind, you typically have the right to withdraw consent and request your data be deleted from databases (though anonymized data already used in research may be harder to retract).
Understanding these rights empowers you to ask informed questions and make decisions aligned with your comfort level.
Key Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
Before participating in AI-driven personalized medicine, ask these critical questions:
- Where will my data be stored, and who has access? Understand if data stays within your healthcare system or gets sent to third-party AI companies. Ask about security measures protecting storage systems.
- Is my data anonymized or identifiable? Anonymized data removes personal identifiers, reducing privacy risks. However, truly anonymous health data is rare—genomic data is inherently identifiable.
- Will my data be used for research beyond my care? Many AI systems improve by learning from patient data. If your information contributes to research, ensure you’re comfortable with this secondary use.
- What happens if there’s a data breach? Ask about notification policies, protections in place, and what support you’d receive if your health data were compromised.
- Can I review the AI’s reasoning? Transparent AI systems should allow you and your doctor to understand why specific treatments were recommended, not just accept them blindly.
- How do you ensure AI recommendations are clinically validated? AI suggestions should always be reviewed by qualified healthcare professionals, not automatically implemented.
These conversations might feel awkward, but responsible healthcare providers welcome questions about data protection. Reluctance to answer clearly should raise red flags about their privacy practices.
Practical Steps to Protect Your Health Data
Beyond asking questions, take proactive measures to safeguard your information:
Review privacy policies carefully. Yes, they’re long and boring, but privacy policies for health AI services contain crucial information about data usage. Look specifically for sections on data sharing, retention periods, and your rights.
Use strong authentication. Health portals and apps accessing your personalized medicine data should require strong passwords and, ideally, two-factor authentication. Never reuse passwords across health and non-health services.
Be cautious with direct-to-consumer genetic testing. Companies offering at-home genetic testing often have different privacy protections than medical providers. Some sell anonymized data to researchers or pharmaceutical companies. Read the terms carefully before sending your DNA.
Understand insurance implications. In many jurisdictions, genetic discrimination by health insurers is illegal, but life insurance and disability insurance may not have the same protections. Consider implications before genetic testing if these insurance types matter to you.
Request data deletion when appropriate. If you participated in a health AI program but no longer need those services, ask whether your data can be deleted rather than retained indefinitely.
Monitor your medical records regularly. Check your health records for accuracy. AI trained on incorrect data will generate flawed recommendations, and errors could affect your care.
Recognizing Responsible AI Implementation
Not all personalized medicine AI systems are created equal. Responsible implementations share common characteristics:
- Transparency: Clear explanations of how AI makes decisions
- Human oversight: Qualified medical professionals review all AI recommendations before implementation
- Regular auditing: Systems are tested for bias and accuracy across diverse patient populations
- Informed consent: Patients receive comprehensive information about data use before participation
- Data minimization: Only information necessary for your treatment is collected, not excessive data “just in case”
- Security certifications: Compliance with healthcare data protection regulations (like HIPAA in the US, GDPR in Europe)
Ask your healthcare provider which of these safeguards are in place. Their presence indicates commitment to ethical AI implementation.

Step-by-Step: How to Engage with Personalized Medicine AI Safely
Now that you understand the fundamentals and privacy considerations, let’s walk through practical steps for safely engaging with AI in Personalized Medicine. Following this structured approach ensures you benefit from these innovations while maintaining control over your health information.
Step 1: Assess Your Healthcare Provider’s AI Capabilities
Before diving into personalized medicine, understand what your current healthcare provider offers. Schedule a conversation with your doctor to discuss:
- What AI-powered personalized medicine services are available in their practice or health system
- Which conditions or treatments they use AI to optimize
- Their experience with these technologies and patient outcomes
- How they integrate AI recommendations with traditional clinical judgment
This initial assessment helps you understand your options and your doctor’s comfort level with these tools. Some providers eagerly embrace AI, while others remain cautious. Neither approach is inherently wrong—what matters is finding a provider whose philosophy aligns with your preferences.
Why this step matters: Not all healthcare providers have equal access to cutting-edge AI systems. Understanding what’s available prevents disappointment and helps you decide whether seeking specialized centers might be worthwhile for your specific condition.
Step 2: Educate Yourself About Your Condition
The more you understand your health condition, the better you can evaluate AI recommendations. Research your diagnosis using reliable sources:
- Medical institutions’ patient education materials
- Peer-reviewed journals (simplified summaries often available)
- Patient advocacy groups for your specific condition
- Evidence-based medicine databases
Understanding standard treatment approaches, common challenges, and emerging therapies helps you have informed conversations about whether personalized AI analysis might benefit you.
Why this step matters: You’re not trying to become your own doctor, but educated patients better advocate for themselves. When AI suggests unconventional treatments based on your unique profile, you’ll understand the reasoning rather than accepting recommendations blindly.
Step 3: Request Comprehensive Data Collection
If you decide to pursue AI-powered personalized treatment, work with your healthcare team to compile comprehensive health information:
Gather existing medical records: Request copies of all relevant medical records, test results, imaging studies, and treatment histories. Many health systems now offer patient portals, making this easier.
Consider genomic testing if recommended: For conditions where genetic information significantly impacts treatment (like cancer, cardiovascular disease, and certain mental health conditions), discuss whether genomic testing would be valuable. Understand costs, insurance coverage, and privacy implications before proceeding.
Track lifestyle and symptom data: Use journals or apps to record diet, exercise, sleep, stress levels, and symptoms. This contextual information enhances AI analysis beyond clinical data alone.
Connect wearable device data if appropriate: If you use fitness trackers or health monitoring devices, ask whether this data can be integrated into your personalized medicine analysis.
Why this step matters: AI is only as good as the data it analyzes. Comprehensive information enables more accurate predictions and personalized recommendations. However, balance thoroughness with comfort—only share data you’re genuinely comfortable having analyzed.
Step 4: Review and Consent to Data Usage Terms
Before any AI analysis begins, carefully review all consent documents and data usage agreements:
Read the entire consent form, not just the signature page. Look specifically for:
- What data will be analyzed
- Where data will be stored and processed
- Who will have access (just your care team, or also third-party AI companies)
- Whether data will be used for research
- How long data will be retained
- Your rights to access, correct, or delete data
Ask questions about anything unclear. Healthcare providers should willingly explain terms in plain language.
Request modifications if needed: Consent forms aren’t always negotiable, but sometimes you can limit certain data uses while still receiving care. For example, you might agree to AI analysis for your treatment but decline broader research participation.
Why this step matters: This is your last chance to ensure you’re comfortable with data practices before proceeding. Once data is analyzed and shared, it’s much harder to retract. Take this decision seriously.
Step 5: Participate in AI-Informed Treatment Planning
Once AI analysis is complete, meet with your healthcare team to review results and recommendations:
Request detailed explanations: Ask your doctor to explain in plain language why the AI recommended specific treatments. What patterns did it identify in your data? How do these recommendations differ from standard approaches?
Understand confidence levels: AI predictions come with probability estimates. Does the system have high confidence in its recommendations, or is it less certain? Understanding this context helps appropriate decision-making.
Discuss alternatives: Even if AI strongly recommends one treatment, ask about alternatives. What would the second-best option be? What would standard non-personalized treatment look like? This comparison helps you appreciate the AI’s value.
Evaluate risks and benefits personally: AI optimizes for clinical outcomes, but you might prioritize different factors—quality of life, side effect tolerance, and treatment burden. Ensure the treatment plan aligns with your values, not just statistical outcomes.
Why this step matters: Personalized medicine AI is a tool to inform decisions, not make them for you. The final treatment choice should be a collaboration between you, your doctor, and the AI insights—with you as the ultimate decision-maker about your body.
Step 6: Monitor Treatment Response and Communicate Changes
As treatment progresses, active participation improves outcomes:
Track your response: Note symptom changes, side effects, and quality of life impacts. Many AI systems incorporate patient-reported outcomes, so your observations directly improve predictions.
Report unexpected effects immediately: If you experience symptoms the AI didn’t predict or known side effects seem more severe than expected, tell your healthcare team promptly. This information helps refine the AI’s models.
Attend follow-up appointments consistently: Regular monitoring allows AI systems to adjust recommendations based on your actual response, not just initial predictions.
Ask about treatment adjustments: If your response differs from predictions, discuss whether treatment modifications would be beneficial. AI-informed care should be dynamic, not static.
Why this step matters: The continuous learning aspect of AI personalized medicine depends on feedback loops. Your experience contributes to improving the system for yourself and future patients.
Step 7: Periodically Reassess Data Sharing and Privacy
Your comfort level with data sharing may change over time. Schedule regular reviews:
Annually review privacy settings: Check what data is still being collected and shared. Do these arrangements still align with your preferences?
Request data access: Exercise your right to see what health information is stored about you. Verify accuracy and completeness.
Update consent preferences if needed: If your feelings about research participation or data sharing have changed, communicate this to your healthcare provider.
Stay informed about breaches: Unfortunately, healthcare data breaches occur. Monitor whether organizations holding your data have experienced security incidents and what protections they’ve added.
Why this step matters: Data security is an ongoing process, not a one-time decision. Regular reassessment ensures your privacy protections evolve with both your preferences and changing technological landscapes.
Common Concerns and How to Address Them
Even with understanding and preparation, many people have legitimate concerns about AI-powered personalized medicine. Let’s address the most common worries with practical solutions.
“What if the AI makes a mistake?”
AI systems can make errors, just like human doctors. However, responsible implementation includes multiple safeguards:
- Healthcare professionals review all AI recommendations before implementation
- Patients can seek second opinions, including from providers not using the same AI system
- Most AI-informed decisions still allow human override if something seems wrong
- Continuous monitoring catches problems early before serious harm occurs
What you can do: Always ensure a qualified healthcare professional is involved in treatment decisions, not AI alone. Trust your instincts—if a recommendation feels wrong, request additional review or seek a second opinion.
“Will insurance companies use my genetic data against me?”
This is a serious concern with nuanced answers depending on your location:
In the United States, the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) prohibits health insurers and employers from discriminating based on genetic information. However, GINA doesn’t cover life insurance, disability insurance, or long-term care insurance.
In the European Union, GDPR provides strong protections for genetic data as a special category requiring explicit consent for processing.
What you can do: Before genetic testing, research your jurisdiction’s specific protections. If you need life or disability insurance, consider purchasing it before undergoing genetic testing. Ask healthcare providers whether genetic information will be included in records accessible to insurers.
“I don’t want my health data used for corporate profit.”
This is a completely reasonable boundary. Data monetization in healthcare is controversial, with valid concerns about companies profiting from patient information without fair compensation.
What you can do: Explicitly ask whether your de-identified data will be sold or licensed to pharmaceutical companies, technology firms, or researchers. Some AI services allow opting out of broader data sharing while still receiving personalized care. If a provider requires data sharing you’re uncomfortable with, consider whether alternative providers offer better terms.
“What if AI reinforces healthcare biases?”
AI trained on historically biased data can perpetuate or even amplify healthcare disparities. This is a genuine concern that responsible developers actively address through:
- Training AI on diverse patient populations
- Regular auditing for bias across different demographics
- Transparency about which populations the AI performs best for
- Continuous refinement as disparities are identified
What you can do: Ask whether the AI system has been validated in populations similar to yours (considering race, ethnicity, gender, age, and socioeconomic factors). Request information about the system’s performance across different groups. If meaningful differences exist, factor this into your decision-making.
The Future of AI in Personalized Medicine: What’s Coming Next
The Role of AI in Personalized Medicine continues to evolve rapidly. Understanding emerging developments helps you anticipate future opportunities and challenges.
Real-Time Continuous Health Monitoring
Wearable and implantable devices combined with AI will enable unprecedented continuous monitoring. Rather than snapshots during clinic visits, AI will analyze your health data constantly, detecting subtle changes indicating problems long before symptoms appear. This shift from reactive to truly preventive medicine could dramatically improve outcomes while reducing healthcare costs.
AI-Discovered Treatments
Beyond optimizing existing therapies, AI is discovering entirely new treatments. Machine learning systems analyze millions of molecular compounds to identify potential drugs far faster than traditional research. Some AI-discovered medications are already in clinical trials. In the future, treatments might be designed specifically for your unique biological profile, not just selected from existing options.
Predictive Disease Prevention
As AI analyzes more longitudinal health data, it’s becoming increasingly accurate at predicting disease development years before symptoms appear. Imagine knowing at age 35 that your specific combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors puts you at high risk for diabetes at age 50—allowing 15 years of personalized prevention rather than treatment after diagnosis.
Democratized Access to Expertise
AI could help address healthcare inequality by bringing specialist-level diagnostic and treatment optimization to underserved areas. A general practitioner in a rural clinic, supported by AI analysis, could provide care approaching the quality of major medical centers. However, this benefit depends on intentional policy and investment—technology alone won’t automatically reduce disparities.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Personalized Medicine
Taking Your First Steps Toward AI-Enhanced Healthcare
The Role of AI in Personalized Medicine represents one of healthcare’s most promising frontiers, offering the possibility of treatments truly tailored to your unique biology and life circumstances. As you’ve learned throughout this guide, engaging with these innovations safely requires balancing enthusiasm with thoughtful attention to privacy, ethics, and personal preferences.
Your journey toward AI-enhanced healthcare begins with education—which you’ve now completed by reading this comprehensive guide. You understand how AI analyzes health data, what questions to ask healthcare providers, how to protect your information, and what to expect from the process. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions aligned with your values and health goals.
Remember that adopting personalized medicine AI is not an all-or-nothing choice. You might start small—perhaps allowing AI analysis of existing medical records to optimize current treatment—before deciding whether to pursue more comprehensive genomic testing or continuous monitoring. There’s no rush, and the technology will only improve with time.
Most importantly, maintain agency throughout the process. These are powerful tools, but they serve you—not the other way around. Never feel pressured to share data you’re uncomfortable sharing, accept recommendations that don’t feel right, or proceed faster than your comfort level allows. The best healthcare, whether AI-enhanced or traditional, respects patient autonomy and prioritizes your well-being above all else.
As someone deeply committed to ethical AI implementation, I encourage you to view yourself as an active participant in shaping how these technologies develop. Your questions, concerns, and feedback to healthcare providers influence how responsibly AI is deployed. By engaging thoughtfully—embracing benefits while insisting on proper safeguards—you contribute to creating a healthcare future that serves everyone fairly and safely.
The future of medicine is increasingly personalized, and AI is accelerating this transformation. By approaching these innovations with informed curiosity rather than blind acceptance or fearful rejection, you position yourself to benefit while protecting what matters most: your health, your privacy, and your right to make autonomous decisions about your care.
References:
– Mishra, A., Majumder, A., Kommineni, D., Joseph, C. A., Chowdhury, T., & Anumula, S. K. (2025). “Role of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Medicine: A Systematic Review.” Cureus, 17(4), e82310. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82310 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40376348/
– Liu, R., et al. (2025). “How AI and Genomics are Personalizing Cancer Treatment.” Nature Communications. University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering. Published February 11, 2025. https://viterbischool.usc.edu/news/2025/02/how-ai-and-genomics-are-personalizing-cancer-treatment/
– Chen, Y., et al. (2025). “Unlocking precision medicine: clinical applications of integrating health records, genetics, and immunology through artificial intelligence.” Journal of Biomedical Science, 32, Article 16. Published February 7, 2025. https://jbiomedsci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12929-024-01110-w
– Rajendran, S., et al. (2025). “AI-Enhanced Predictive Imaging in Precision Medicine: Advancing Diagnostic Accuracy and Personalized Treatment.” iRADIOLOGY. Published July 11, 2025. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ird3.70027
– StartUs Insights. (2025). “10 Emerging Trends in Precision Medicine [2025].” Published May 16, 2025. https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/trends-in-precision-medicine/
– HUSPI. (2025). “Personalized Medicine 2025: How AI Will Change the Doctors’ Approach to Treatment.” Published September 26, 2025. https://huspi.com/blog-open/personalized-medicine-how-ai-will-change-the-doctors-approach-to-treatment/
– Research and Markets. (2025). “Precision Medicine Strategic Intelligence Report 2025: Opportunities in Integrating AI and Bioinformatics to Predict Disease Risks, Enhance Diagnostics, and Shape Personalized Care.” Published November 25, 2025. https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2025/11/25/3194434/28124/en/Precision-Medicine-Strategic-Intelligence-Report-2025-Opportunities-in-Integrating-AI-and-Bioinformatics-to-Predict-Disease-Risks-Enhance-Diagnostics-and-Shape-Personalized-Care.html
– Sharma, R., & Patel, K. (2025). “Artificial Intelligence in Precision Medicine and Patient-Specific Drug Design.” Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal. Published February 20, 2025. https://biomedpharmajournal.org/vol18marchspledition/artificial-intelligence-in-precision-medicine-and-patient-specific-drug-design/
– Zheng, L., et al. (2025). “Advancing precision oncology with AI-powered genomic analysis.” Frontiers in Pharmacology. Published April 21, 2025. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1591696/full
– García-Ruiz, M., et al. (2025). “From Genomics to AI: Revolutionizing Precision Medicine in Oncology.” Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6578. Published June 11, 2025. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/15/12/6578
– OncoDaily. (2025). “How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Cancer Care in 2025: Diagnosis, Treatment, Clinical Trials, and Screening.” Published June 10, 2025. https://oncodaily.com/oncolibrary/artificial-intelligence-ai
– Li, H., et al. (2025). “Current AI technologies in cancer diagnostics and treatment.” Molecular Cancer. Published June 2, 2025. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12943-025-02369-9
– Ethical and Legal Considerations Working Group. (2025). “Ethical and legal considerations in healthcare AI: innovation and policy for safe and fair use.” Royal Society Open Science. Published May 2025. https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsos.241873 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12076083/
– Mayover, T. L. (2025). “When AI Technology and HIPAA Collide.” HIPAA Journal. Published May 2, 2025. https://www.hipaajournal.com/when-ai-technology-and-hipaa-collide/
– Foley & Lardner LLP. (2025). “HIPAA Compliance for AI in Digital Health: What Privacy Officers Need to Know.” Published May 14, 2025. https://www.foley.com/insights/publications/2025/05/hipaa-compliance-ai-digital-health-privacy-officers-need-know/
– Ailoitte. (2025). “GDPR-Compliant AI in Healthcare: A Guide to Data Privacy.” Published May 15, 2025. https://www.ailoitte.com/insights/gdpr-compliant-healthcare-application/
– Inquira Health. (2025). “GDPR and HIPAA Compliance in Healthcare AI: What IT Leaders Must Know.” Published March 31, 2025. https://www.inquira.health/en/blog/gdpr-and-hipaa-compliance-in-healthcare-ai-what-it-leaders-must-know
– Compass IT Compliance. (2025). “HIPAA Compliance in 2025: What’s Changing & Why It Matters.” Published July 10, 2025. https://www.compassitc.com/blog/hipaa-compliance-in-2025-whats-changing-why-it-matters
– Healthcare Data Privacy Research Team. (2025). “Data privacy in healthcare: Global challenges and solutions.” PMC. Published 2025. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12138216/
– ResearchGate. (2025). “AI and Data Privacy in Healthcare: Compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and emerging regulations.” Published May 18, 2025. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/392617572_AI_and_Data_Privacy_in_Healthcare_Compliance_with_HIPAA_GDPR_and_emerging_regulations
– Personalized Medicine Coalition (PMC). (2025). “Personalized Medicine Report on 2024 FDA Approvals.” Published 2025. Referenced in: https://huspi.com/blog-open/personalized-medicine-how-ai-will-change-the-doctors-approach-to-treatment/
– National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2025). “AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF).” Referenced in: https://www.hipaajournal.com/when-ai-technology-and-hipaa-collide/

About the Author
Nadia Chen is an expert in AI ethics and digital safety, specializing in helping non-technical individuals navigate emerging technologies responsibly. With a background in both healthcare informatics and privacy advocacy, Nadia focuses on empowering patients to benefit from AI innovations while maintaining control over their personal health information. She believes that technological advancement and ethical implementation are not just compatible but essential partners in creating healthcare that truly serves everyone. Through clear, accessible writing, Nadia translates complex AI concepts into practical guidance that helps people make informed decisions about their digital health future.