How to Document Statistical Significance & Learnings Using AI
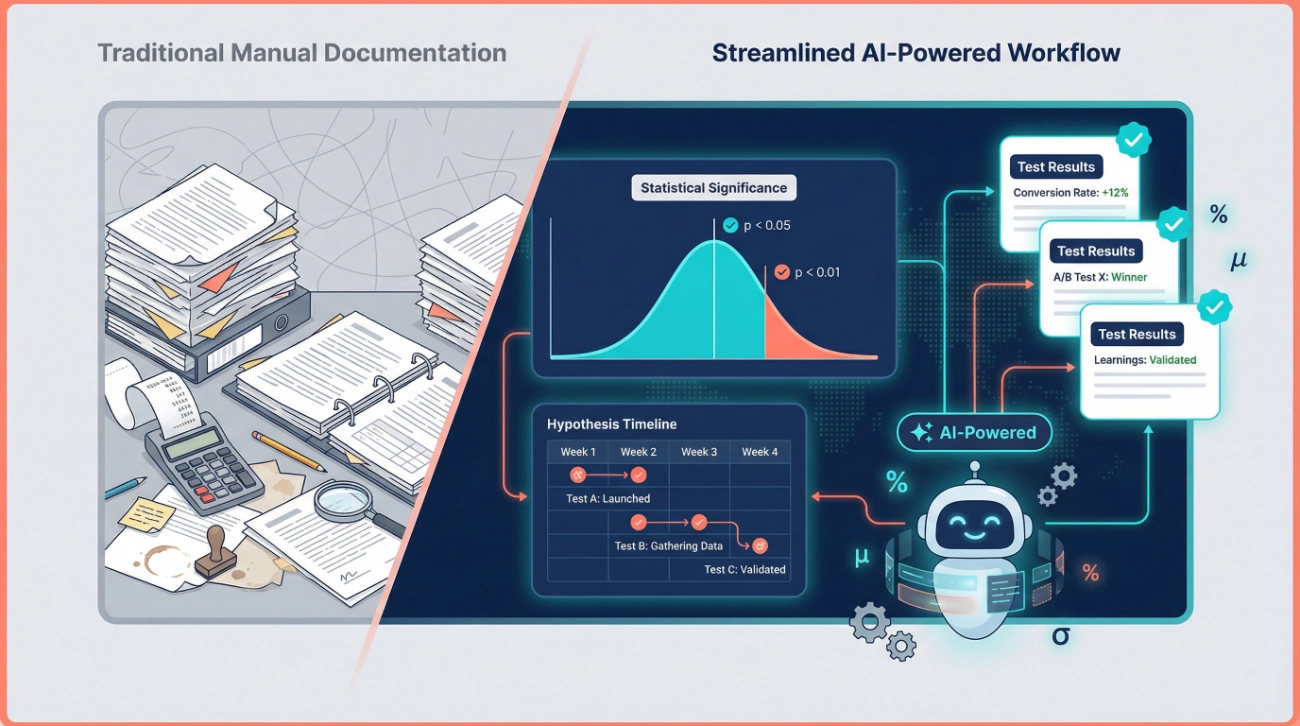
How to Document Statistical Significance & Learnings Using AI starts with a simple truth: your testing program is only as valuable as the documentation you keep. We’ve spent years running A/B tests, analyzing control versus test variations, and building hypothesis calendars—and we’ve learned that AI transforms this entire workflow from tedious manual work into an automated, intelligent system.
The challenge isn’t just running tests anymore. According to McKinsey in their “The State of AI in 2025: Agents, Innovation, and Transformation” report (2025), 88 percent of organizations now use AI in at least one business function—up from 78 percent just one year ago. ℹ️Source
The real opportunity lies in documenting your learning systematically, so future tests build on past insights rather than repeating the same mistakes. We’re going to show you exactly how to leverage AI tools to capture statistical significance, organize test results, extract actionable lessons, and create a hypothesis calendar that keeps your optimization program running smoothly month after month.
Why Documenting Test Results Matters More Than You Think
Before we dive into the how-to steps, let’s address why documentation deserves your attention. We’ve seen countless marketing teams run brilliant tests only to forget what they learned three months later. The result? They test the same variables again, waste budget, and lose momentum.
Proper documentation serves three critical purposes. First, it creates an institutional memory that survives team turnover. When someone new joins your team, they can review past tests and understand what works for your audience without starting from scratch. Second, documentation helps you spot patterns across multiple tests. You might discover that certain types of headlines consistently perform better or that specific audience segments respond differently to the same changes. Third, maintaining detailed records prevents you from repeating failed experiments and allows you to build on successful ones.
The businesses capturing real value from testing aren’t just running more experiments—they’re learning faster because they document systematically. This is where AI becomes transformative.
What You’ll Need to Get Started
Let’s talk about the tools and setup. You don’t need an expensive enterprise solution or a data science degree. We approach this practically, choosing tools that integrate with your existing workflow.
Essential Tools for AI-Powered Documentation:
For statistical analysis and documentation, consider tools like Julius AI, which works with spreadsheets and datasets using plain language queries, or DataStatPro’s AI statistical analysis platform that automatically recommends appropriate tests and provides plain-language interpretations. ChatGPT can also assist with result interpretation and documentation formatting, though outputs should always be verified.
For organizing hypothesis calendars, you can use AI-enhanced project management tools that integrate with your testing platform. Google Sheets with AI formulas works perfectly for smaller teams, while larger organizations might benefit from dedicated testing platforms like Optimizely or VWO that include built-in documentation features.
For data visualization, Polymer transforms spreadsheets into interactive dashboards automatically, while Tableau and Power BI offer AI-powered insights for more complex analysis needs.
The beauty of modern AI tools is that they work with your existing data. You don’t need to migrate everything to a new system—you can start documenting better today with the tools you already have.
Step 1: Set Up Your Testing Documentation Framework
How to Document Statistical Significance & Learnings Using AI begins with establishing a consistent structure. We recommend creating a master spreadsheet or database that captures essential information for every test you run.
Your documentation framework should include these core elements:
Test Identification Information:
Assign each test a unique ID number, record the test name and description, note which page or element you’re testing, and document the date range when the test ran.
Hypothesis Documentation:
Write out your complete hypothesis statement following this format:If we [change X], then [Y metric] will [increase/decrease] because [reason based on user behavior].This forces you to think through why you expect a certain outcome, not just what you’re testing.
Document your expected impact—be specific about the percentage lift you anticipate. Record the priority level of this test compared to others in your queue.
Test Setup Details:
Note which variations you tested (Control A, Variation B, etc.).
Document the traffic allocation (typically 50/50, but record whatever split you used).
Specify which audience segments saw the test (all visitors, mobile only, new users, etc.).
List any filters applied (exclude employees, remove outliers, etc.).
Results and Statistical Significance:
This is where AI becomes incredibly valuable. Instead of manually calculating p-values and confidence intervals, AI tools can analyze your raw data and provide instant statistical interpretation.
Feed your test data into an AI statistical tool and document:
- The conversion rate for each variation has exact percentages.
- The sample size for each group.
- The statistical significance level (typically you want a p-value < 0.05).
- The confidence interval for your results.
- Any segments where results differed significantly.
AI tools excel at catching errors in statistical interpretation that humans miss. They’ll flag insufficient sample sizes, remind you about multiple comparison corrections, and alert you to potential confounding variables.
Learning and Next Steps: Perhaps the most critical section. Document what you learned even from “failed” tests. Record which variation won and by how much. Note any unexpected findings or surprises. Write down your hypothesis for the next test based on these results. Specify the recommended action (implement winner, run follow-up test, abandon this approach).
We’ve found that the “learnings” section separates good testing programs from great ones. Don’t just record numbers—capture the insights that will inform future decisions.
Step 2: Use AI to Interpret Statistical Significance Automatically
One of the biggest bottlenecks in test documentation is calculating and interpreting statistical significance. Most marketers aren’t statisticians, and manual calculation invites errors.
Here’s exactly how to use AI to handle this automatically:
Upload Your Raw Test Data:
Export your test results as a CSV or Excel file containing visitor counts per variation, conversion counts per variation, dates, and any relevant segmentation data.
Choose Your AI Analysis Tool:
For quick analysis, ChatGPT can calculate significance if you provide the numbers and ask it to run a two-proportion z-test or chi-square test. For more robust analysis, dedicated tools like DataStatPro or Julius AI understand statistical context better and provide more detailed explanations.
Ask the Right Question:
Don’t just upload data and hope for insights. Be specific with your prompt:I ran an A/B test with the following results: Control had 1,247 visitors and 87 conversions. Variation B had 1,289 visitors and 112 conversions. Calculate the statistical significance using a 95% confidence level and explain whether this result is reliable enough to implement.
The AI will automatically:
Calculate conversion rates for both variations. Determine the p-value. Tell you whether the result reaches statistical significance. Explain what the confidence interval means in plain language. Flag any concerns about sample size or test duration.
Document the AI’s Interpretation:
Copy the key findings into your documentation framework. Save the complete analysis output as a reference file. Highlight any cautions or limitations the AI identified.
One critical advantage: AI tools can run multiple statistical tests simultaneously and tell you which one is most appropriate for your data structure. They’ll differentiate between scenarios requiring t-tests versus chi-square tests versus ANOVA, something that confuses many practitioners.
However, always apply human judgment. AI is excellent at crunching numbers, but you understand the business context. If AI says a 2% improvement is statistically significant but you know seasonal factors might have influenced the result, document that caveat.

Step 3: Extract and Categorize Learnings Systematically
Raw numbers tell you what happened. Learnings explain why it matters and what to do next. This is where AI shifts from being a calculator to being a strategic partner.
Set Up Learning Categories:
Before analyzing results, establish categories for organizing insights. We use these five categories: audience insights (what we learned about user behavior), messaging insights (which language or positioning resonated), design insights (visual or UX learnings), technical insights (performance or functionality discoveries), and negative learnings (what definitely didn’t work).
Use AI to Identify Patterns:
Feed your AI tool the complete context of your test along with the results and ask it to identify patterns:Here's the hypothesis, test setup, and results from my landing page test. Analyze these results and identify: (1) Why the variation might have performed better, (2) Any patterns in the segment-level data, (3) What this suggests about user behavior, (4) What we should test next.
The AI will provide hypotheses about why certain changes worked. For example, if your test showed that adding social proof above the fold increased conversions by 18%, AI might suggest that your audience has high trust concerns and recommend testing other trust-building elements like security badges or guarantees.
Cross-Reference Historical Tests:
This is where systematic documentation pays dividends. Ask your AI tool to compare current results with past tests: “Review our last six tests on pricing pages. Do the latest results confirm or contradict previous patterns? What should we conclude about how our audience responds to price anchoring?”
AI excels at spotting connections across multiple data points that humans might miss. It might notice that headline tests always perform better on mobile than on desktop or that urgency messaging works for new visitors but not returning customers.
Document Contradictions and Anomalies:
Sometimes tests produce unexpected results. When your AI analysis reveals something that contradicts your hypothesis or previous learnings, document it prominently. These anomalies often lead to breakthrough insights.
For instance, if you expected that shortening your form would increase conversions but the longer form actually won, ask AI to help theorize why. It might suggest that the additional fields qualified leads better, reducing post-conversion drop-off—an insight worth investigating further for conversions.
Want a structured approach to test execution that you can apply right away? Our A/B Test Execution & Analysis Checklist walks you through each phase from setup to documentation, helping you avoid common mistakes and make data-driven decisions faster.
Step 4: Build an AI-Enhanced Hypothesis Calendar
A hypothesis calendar transforms testing from reactive to strategic. Instead of wondering, “what should we test next?” you’ll have a pipeline of prioritized experiments ready to deploy.
Here’s how to build yours with AI assistance:
Start With Your Learnings Database: Review all documented tests and learnings. Ask your AI tool to analyze this data and suggest hypothesis categories worth exploring.
The prompt might be:Based on these 15 completed tests, identify the top three areas where we have limited data and suggest hypothesis statements for each area.
AI is particularly good at spotting gaps in your testing coverage. You might have tested headlines extensively but never touched the pricing display, or you might have tested desktop layouts while ignoring mobile user flows.
Generate Hypothesis Statements:
For each identified opportunity, use AI to craft proper hypothesis statements. A well-formed hypothesis follows this structure:If we [specific change], then [specific metric] will [increase/decrease] by [estimated amount] because [behavioral reason].
AI can help refine vague ideas into testable hypotheses. If you say, “we want to test the signup button,” it could suggest:
If we change the signup button copy from 'Get Started' to 'Start Your Free Trial', then click-through rate will increase by 12% because it makes the zero-risk nature of the trial more explicit.Prioritize Using AI-Driven Frameworks: Not all tests deserve equal priority. Feed your list of hypotheses into an AI tool along with information about your traffic levels, current conversion rates, and business goals. Ask it to score each hypothesis using the PIE framework (Potential impact, Importance to business, Ease of implementation) or ICE framework (Impact, Confidence, Ease).
The AI will provide numerical scores and rankings, helping you focus resources on high-value tests first.
Create Your Monthly/Quarterly Calendar: Map out which tests you’ll run when. AI can help optimize the sequence.
Ask:Given these 12 hypothesis statements with their priority scores, create a testing calendar for the next three months that maximizes learning velocity. Consider that tests need 2-3 weeks minimum to reach statistical significance, and some tests build on insights from others.
The AI will suggest an intelligent sequence, perhaps running quick-win tests early to build momentum while scheduling dependent tests in logical order.
Build in Review Cycles: Your hypothesis calendar shouldn’t be static. Schedule monthly reviews where AI helps you reassess priorities based on new learnings. Results from Test A might change the priority of Test F dramatically.

Step 5: Automate Control vs. Test Comparisons
Comparing control and test variations accurately is fundamental to reliable testing. AI eliminates the tedious manual work while catching comparison errors that humans often miss.
Structure Your Comparison Template:
Create a standardized template that AI can populate automatically. Include sections for primary metric comparison (typically conversion rate), secondary metrics (time on page, bounce rate, revenue per visitor), segment breakdowns (mobile vs desktop, new vs returning, geographic regions), and statistical confidence for each comparison.
Feed Raw Data to AI Tools:
Export your testing platform data or analytics data as structured files. Most AI tools can process CSV, Excel, or JSON formats. The data should include timestamps, visitor IDs or session IDs, variation assignments, and conversion events.
Automate the Analysis:
Use AI to run comprehensive comparisons automatically.
Here’s an effective prompt structure:Compare Control A and Variation B across all key metrics. For each metric, calculate the absolute difference, the percentage change, and the statistical significance, and flag any segments where the difference exceeded 10%.
The AI will generate a complete comparison table showing exactly where the variations differed and whether those differences matter statistically.
Visualize Results:
Ask AI to suggest the best visualization for your specific results. It might recommend a bar chart for conversion rate comparisons, a line graph for time-series data showing how the gap evolved during the test, or a heatmap showing segment-level performance.
Many AI tools can generate these visualizations directly. ChatGPT with Advanced Data Analysis can create charts based on your data. Julius AI specializes in creating visual representations of statistical findings.
Document Edge Cases:
AI is excellent at identifying unusual patterns. It might notice that while the overall test showed a 5% lift, one particular segment saw a 40% improvement while another declined by 15%. These edge cases often reveal the most intriguing insights.
Step 6: Create Automated Learning Summaries
After every test, create a summary that anyone on your team can understand—even if they weren’t involved in running the experiment. AI makes this process fast and consistent.
Prompt AI to Generate Executive Summaries:
After documenting your detailed results, ask AI to create concise summaries:Summarize this A/B test in three sections: (1) What we tested and why in two sentences, (2) Key results in bullet points, (3) Recommended action in one sentence.
The AI will distill pages of documentation into a scannable summary that busy stakeholders can review in 30 seconds.
Generate Learning Cards:
Create bite-sized insight cards that capture one learner per card. These work excellently for sharing across teams or posting in Slack channels.
Ask AI:Create a learning card from this test with a headline stating the insight, three supporting data points, and one actionable recommendation.
For example:
Headline: Social Proof Above Fold Increases Trust for New Visitors.
Data: 23% conversion lift among first-time visitors, No significant change for returning visitors, Mobile users showed stronger response (31% lift).
Action: Test additional trust signals specifically for new mobile traffic.Build a Searchable Knowledge Base:
Compile all your learning summaries into a searchable repository. Many teams use Notion, Confluence, or Google Docs.
Add tags that AI can generate automatically based on content: test type, page tested, primary insight category, and result (winner/loser/inconclusive).
Later, when planning new tests, you can query this knowledge base through AI:
What have we learned about pricing page optimization in the past year?The AI can search your documentation and synthesize findings across multiple tests.
Looking to accelerate your entire AI content workflow beyond just testing documentation? Download our 100+ AI Marketing Prompts collection with ready-to-use templates for content creation, analysis, and optimization. These are the exact prompts we use with solo entrepreneurs, creators, and agencies to save hours of work every week.
Step 7: Set Up Automated Alerts for Pattern Recognition
One of AI’s most powerful capabilities is recognizing patterns across datasets too large for humans to process efficiently. Set up automated pattern recognition to surface insights you might otherwise miss.
Configure Pattern-Detection Prompts:
Create standing prompts that AI runs monthly against your complete testing database:Analyze all tests from the past 90 days and identify: any metrics that consistently moved in unexpected directions, any variations that performed significantly differently across segments, any test outcomes that contradict our hypotheses, any learnings that repeat across multiple tests.
Track Metric Correlations:
Ask AI to identify which changes tend to move together:When conversion rate increases, what other metrics typically change? Are there any inverse correlations in our data?You might discover that tests improving conversion rate often slightly increase bounce rate, suggesting users are making faster decisions, or that mobile improvements rarely translate to desktop.
Monitor Seasonal Patterns:
If you’ve been testing for multiple quarters, AI can detect seasonal influences: “Compare test results from Q1 across the past two years. Do certain types of tests perform better or worse during this period?”
Understanding seasonal patterns prevents you from incorrectly attributing results to test variations when timing explains the change.
Flag Anomalies Requiring Investigation:
Set AI to alert you when results deviate significantly from established patterns. If headline tests usually generate 5-15% lifts but suddenly one shows a 45% improvement, AI should flag this for more profound investigation. Anomalies might indicate technical errors, external factors, or genuine breakthrough insights.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Documenting with AI
We’ve made plenty of mistakes implementing AI-powered documentation, and we can help you avoid them:
Over-Trusting AI Without Verification:
AI occasionally hallucinates statistics or misinterprets data. Always spot-check critical numbers.
If AI reports a p-value of 0.03, verify using a traditional calculator.
If it claims a 50% conversion lift, ensure that figure appears in your raw data.
Documenting Too Little Context:
AI needs context to provide useful analysis.
Don’t just feed it numbers—include information about what changed, why you tested it, what you expected to happen, and any external factors that might have influenced results.
Forgetting to Document Inconclusive Tests:
Failed and inconclusive tests teach you as much as winners.
Document why a test failed to reach statistical significance.
Was the sample size too small? Was the variation too subtle?
Did external factors contaminate results?
Future you will thank present you for this documentation.
Not Standardizing Your Documentation Format:
If every test uses a different documentation structure, AI struggles to identify patterns across tests.
Stick to your framework religiously.
Ignoring Qualitative Insights:
AI excels with quantitative data but can miss qualitative signals.
Supplement AI analysis with customer feedback, session recordings, and team observations.
Note these qualitative insights in your documentation alongside statistical findings.
Advanced Techniques: Multi-Variant Testing Documentation
Once you’re comfortable documenting simple A/B tests, you can apply the same principles to multivariate tests and more complex experiments.
For tests with three or more variations, AI becomes even more valuable because the number of comparisons grows exponentially. A three-way test requires three pairwise comparisons. A five-way test requires ten.
Prompt AI for Comprehensive Multi-Variant Analysis:
I ran a test with one control and four variations. Analyze all pairwise comparisons, identify which variations performed statistically better than control, rank all five variations by performance, and determine if any variations performed statistically similarly to each other.
The AI will generate a complete ranking with confidence levels for each comparison, saving hours of manual statistical work.
Document Interaction Effects:
In multivariate tests where you change multiple elements simultaneously, interaction effects matter.
AI can help identify these:In this multivariate test changing both the headline and CTA button, determine whether the two elements interact or if their effects appear independent.
If headline change drives most of the improvement regardless of button variation, document that the button change had minimal impact. If certain headline-button combinations performed much better than expected, document that insight separately.
Integrating Your Documentation System with Your Testing Stack
How to Document Statistical Significance & Learnings Using AI works best when integrated with your existing tools rather than creating a separate silo.
Most testing platforms (Optimizely, VWO, Google Optimize, and Unbounce) allow data export. Set up automated exports so raw data flows to your documentation system weekly. Use tools like Zapier or Make to trigger AI analysis automatically when new test data appears.
For example, configure a workflow where test completion in VWO triggers an export to Google Sheets, which triggers a Zapier automation, which sends data to your AI tool via API, which generates a statistical analysis and learning summary, which gets posted to your documentation repository, and a notification gets sent to Slack.
This turns documentation from a manual chore into an automatic background process.
Real-World Example: Building Your First AI-Documented Test
Let’s walk through a complete example showing all steps in action.
The Test: You’re testing whether adding a progress bar to a multi-step checkout reduces cart abandonment.
Hypothesis:
If we add a visual progress bar showing users they're on step 2 of 4, then checkout completion rate will increase by 8% because users will have clearer expectations about the checkout process length.
Test Setup Documented:
Test ID: CHECKOUT-042.
Pages: Checkout flow steps 2-4.
Traffic: 50/50 split, all users.
Date range: January 15-29, 2025.
Sample size target: 1,200 completions, minimum.
Running the Test:
Export data when you reach your sample target. Feed it to your AI tool:Analyze this checkout test data. Control had 2,453 users starting checkout with 1,198 completing (48.8% completion rate). Variation with progress bar had 2,501 users starting with 1,312 completing (52.5% completion rate). Calculate statistical significance and recommend whether to implement.
AI Response:
The variation showed a 3.7 percentage point improvement (7.6% relative increase). Using a two-proportion z-test, p-value = 0.012 (statistically significant at 95% confidence level). The result is reliable. Recommend implementing the progress bar. Segment analysis shows stronger effect on mobile users (9.2% relative increase) versus desktop (5.1% relative increase).
Documented Learning:
Category: UX Insights. Key finding:
Progress indicators reduce friction in multi-step processes.
Quantified impact: 7.6% improvement in checkout completion.
Segment insight: Mobile users benefit more from progress clarity.
Next hypothesis:If we add estimated time remaining at each checkout step for mobile users, completion rate will increase by an additional 4% because it reduces mobile users' uncertainty about process length.
Added to Hypothesis Calendar: Scheduled for March 2025 as a follow-up test building on this learning.
This example shows how AI accelerates every step while maintaining rigor and creating institutional knowledge.
FAQ: Documenting Statistical Significance & Learnings Using AI
Your Next Steps: From Documentation to Action
You now have a complete framework for documenting statistical significance and learning using AI. The transformation from manual, inconsistent test documentation to an automated, intelligent system doesn’t happen overnight, but you can start immediately.
Begin with your next test. Set up the basic documentation framework outlined in Step 1. Use a free AI tool like ChatGPT to analyze your results as described in Step 2. Document one: clear learning following the template in Step 3. That’s enough to build momentum.
Within a month, you’ll be documenting two to three tests showing patterns. Within a quarter, you’ll have a hypothesis calendar driving your optimization roadmap. Within six months, you’ll wonder how you ever managed testing without systematic AI-powered documentation.
The competitive advantage doesn’t come from running more tests—it comes from learning faster than your competitors. Documentation is how you learn. AI is how you make documentation effortless.
The businesses pulling ahead aren’t necessarily testing more—they’re simply documenting better, learning faster, and building institutional knowledge that compounds over time. With AI handling the heavy analytical lifting, you can focus your energy on asking better questions, crafting sharper hypotheses, and making smarter strategic decisions.
Start documenting your next test using these principles. Your future self will thank you when you can instantly access insights from dozens of tests instead of struggling to remember what you learned three months ago. The tools exist. The methodology works. The only question is whether you’ll implement it.
About the Authors
This article was written as a collaboration between Alex Rivera (Main Author) and Abir Benali (Co-Author).
Alex Rivera is a creative technologist passionate about making AI accessible to non-technical users. With a focus on step-by-step guidance and practical applications, Alex helps marketers and business owners leverage AI tools to improve their workflows, generate better content, and make data-driven decisions without requiring technical expertise.
Abir Benali is a technology writer specializing in clear, actionable guides for everyday users. Abir’s approach focuses on demystifying complex tools through simple language and real-world examples, helping readers implement AI solutions with confidence even without prior technical knowledge.
Together, we combine creative problem-solving with practical clarity to show you exactly how to document your testing program using AI—making powerful analytics accessible to teams of any size or technical background.